New Insights From Imputed Whole-Genome Sequence-Based Genome-Wide Association Analysis and Transcriptome Analysis: The Genetic Mechanisms Underlying Residual Feed Intake in Chickens.
Poultry feed constitutes the most important price in poultry manufacturing, estimated to be as much as 70% of the whole price. Moreover, there’s strain on the poultry business to extend manufacturing to fulfill the protein demand of people and concurrently scale back emissions to guard the surroundings.
Therefore, enhancing feed effectivity performs an essential function to enhance income and the environmental footprint in broiler manufacturing.
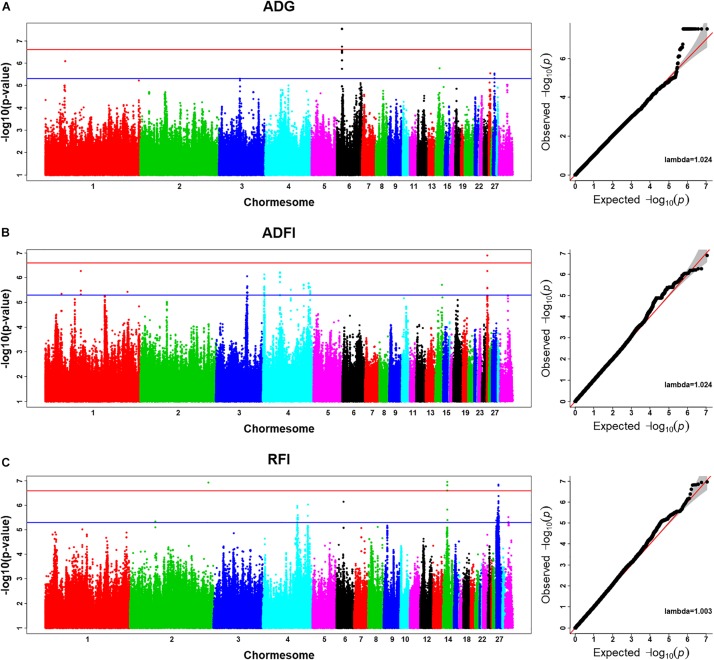
In this research, utilizing imputed whole-genome sequencing knowledge, genome-wide affiliation evaluation (GWAS) was carried out to establish single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and genes related to residual feed consumption (RFI) and its element traits. Furthermore, a transcriptomic evaluation between the high-RFI and the low-RFI teams was carried out to validate the candidate genes from GWAS.
The outcomes confirmed that the heritability estimates of common every day achieve (ADG), common every day feed consumption (ADFI), and RFI have been 0.29 (0.004), 0.37 (0.005), and 0.38 (0.004), respectively. Using imputed sequence-based GWAS, we recognized seven important SNPs and 5 candidate genes [MTSS I-BAR domain containing 1, folliculin, COP9 signalosome subunit 3, 5′,3′-nucleotidase (mitochondrial), and gametocyte-specific factor 1] related to RFI, 20 important SNPs and one candidate gene (inositol polyphosphate multikinase) related to ADG, and one important SNP and one candidate gene (coatomer protein complicated subunit alpha) related to ADFI. After performing a transcriptomic evaluation between the high-RFI and the low-RFI teams, each 38 up-regulated and 26 down-regulated genes have been recognized in the high-RFI group.
Furthermore, integrating regional conditional GWAS and transcriptome evaluation, ras-related dexamethasone induced 1 was the one overlapped gene related to RFI, which additionally recommended that the area (GGA14: 4767015-4882318) is a brand new quantitative trait locus related to RFI.
In conclusion, utilizing imputed sequence-based GWAS is an environment friendly technique to establish important SNPs and candidate genes in rooster. Our outcomes present precious insights into the genetic mechanisms of RFI and its element traits, which might additional enhance the genetic achieve of feed effectivity quickly and cost-effectively in the context of marker-assisted breeding choice.
Genome-wide genetic construction and choice signatures for coloration in 10 conventional Chinese yellow-feathered rooster breeds.
Yellow-feathered chickens (YFCs) have an extended historical past in China. They are well-known for the dietary and business significance attributable to their yellow coloration phenotype. Currently, there’s a big paucity in data of the genetic determinants liable for phenotypic and biochemical properties of those iconic chickens.
This research aimed to uncover the genetic construction and the molecular underpinnings of the YFCs trademark coloration.The whole-genomes of 100 YFCs from 10 main conventional breeds and 10 Huaibei partridge chickens from China have been re-sequenced. Comparative inhabitants genomics based mostly on autosomal single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) revealed three geographically based mostly clusters among the many YFCs.
Compared to different Chinese indigenous rooster genomes integrated from earlier research, a more in-depth genetic proximity inside YFC breeds than between YFC breeds and different rooster populations is clear. Through genome-wide scans for selective sweeps, we recognized RALY heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (RALY), leucine wealthy repeat containing G protein-coupled receptor 4 (LGR4), solute provider household 23 member 2 (SLC23A2), and solute provider household 2 member 14 (SLC2A14), apart from the classical beta-carotene dioxygenase 2 (BCDO2), as main candidates pigment figuring out genes in the YFCs.
We present the primary complete genomic knowledge of the YFCs. Our analyses present phylogeographical patterns among the many YFCs and potential candidate genes giving rise to the yellow coloration trait of the YFCs. This research lays the muse for additional analysis on the genome-phenotype cross-talks that outline essential poultry traits and for formulating genetic breeding and conservation methods for the YFCs.
Related Posts

Exploring the genetic architecture of feed efficiency traits in chickens

Genetic and biological characterisation of three cryptic Eimeria operational taxonomic units that infect chickens (Gallus gallus domesticus)